Expand (xy)^4 Use the Binomial Theorem Simplify each term Tap for more steps Rewrite using the commutative property of multiplication Multiply by Apply the product rule to Rewrite using the commutative property of multiplication Raise to the power of Multiply byIf we expand (ab)(ab) we will get a²b²The procedure to use the binomial expansion calculator is as follows Step 1 Enter a binomial term and the power value in the respective input field Step 2 Now click the button "Expand" to get the expansion Step 3 Finally, the binomial expansion will be displayed in the new window

2 X Square Y Square 8 Z Square 2 Root 2 X Y 4 Root 2 Y Z 8 X Z Brainly In
Expand 2 x + 3 y - 4 z whole square
Expand 2 x + 3 y - 4 z whole square-If we need to calculate variance byCORRECTION Answer b is incorrect the correct answer is 4a^2 12a9Thanks Aditi JainAlgebraic Identities https//wwwyoutubecom/watch?v=HQWggFJVmKQ&list=PL



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions Download Free Pdf
Expand (x 2y z) 2 Solution (x 2y z) 2 is in the form of (a b c) 2 Comparing (a b c) 2 and (x 2y z) 2, we get a = x b = 2y c = z Write the formula / expansion for (a b c) 2 (a b c) 2 = a 2 b 2 c 2 2ab 2bc 2ac Substitute x for a, 2y for b and z for c (x 2y z) 2First remove a common factor Then factor the difference of two squares e) 32 m2n − 50 n3 = 2n(16m2 − 25n2) = 2n(4m 5n) (4m − 5n) The entire figure on the left is a square on side a The square b2 has been inserted in the upper left corner, so that the shaded area is the difference of the two squares, a2 − b2Steps for Solving Linear Equation y = 3x 4 y = 3 x 4 Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side Swap sides so that all variable terms are on the left hand side 3x4=y 3 x 4 = y Subtract 4 from both sides Subtract 4 from both sides
May 29, 18Transcript Example Expand (4a – 2b – 3c)2 (4a – 2b – 3c)2 = (4a (–2b) (–3c)) 2 Using (x y z)2 = x2 y2 z2 2xy 2yz 2zx Putting x = 4aAnd now solve the difference of two squares with a = 36 and b = 4y 2 Solution Factor the equation (rearranged) 36 − 4 y 2 using the identity a 2 − b 2 = ( a b) ( a − b) First factor out the GCF 4 ( 9 − y 2) Both terms are perfect squares so from a 2 b 2 we can find a and bMultiply as we do multiplication of two binomials and we get = a (a b) b (a b) = a 2 ab ab b 2 Add like terms and we get = a 2 2ab b 2 Rearrange the terms and we get = a 2 b 2 2ab Hence, in this way we obtain the identity ie (a b) 2 = a 2 b 2 2ab Following are few applications this identity
Expand following, using suitable identities (x 2y 4z) 2 Advertisement Remove all ads Solution Show Solution It is known that, (x y z) 2 = x 2 y 2 z 2 2xy 2yz 2zx (x 2y 4z) 2 = x 2 (2y) 2 (4z) 2 2(x)(2y) 2(2y)(4z) 2(4z)(x) = x 2 4y 2 16z 2Factorization of x 3 y 3 It can be seen in most book that x 3 y 3 can be factorized by dividing the expression by (x y) After division we get a quotient of (x 2 xy y 2) with no remainder Therefore However, this method involves knowing the factor (x y) beforehand (and the understanding of Factor Theorem)59 = 625 Given, ab bc ca = 59 a 2 b 2 c 2 118 = 625 a 2 b 2 c 2 118 – 118 = 625 – 118 subtracting 118 from both the sides Therefore, a 2 b 2 c 2 = 507 Thus, the formula of square of a trinomial will help us to expand 7th Grade Math Problems 8th Grade Math Practice
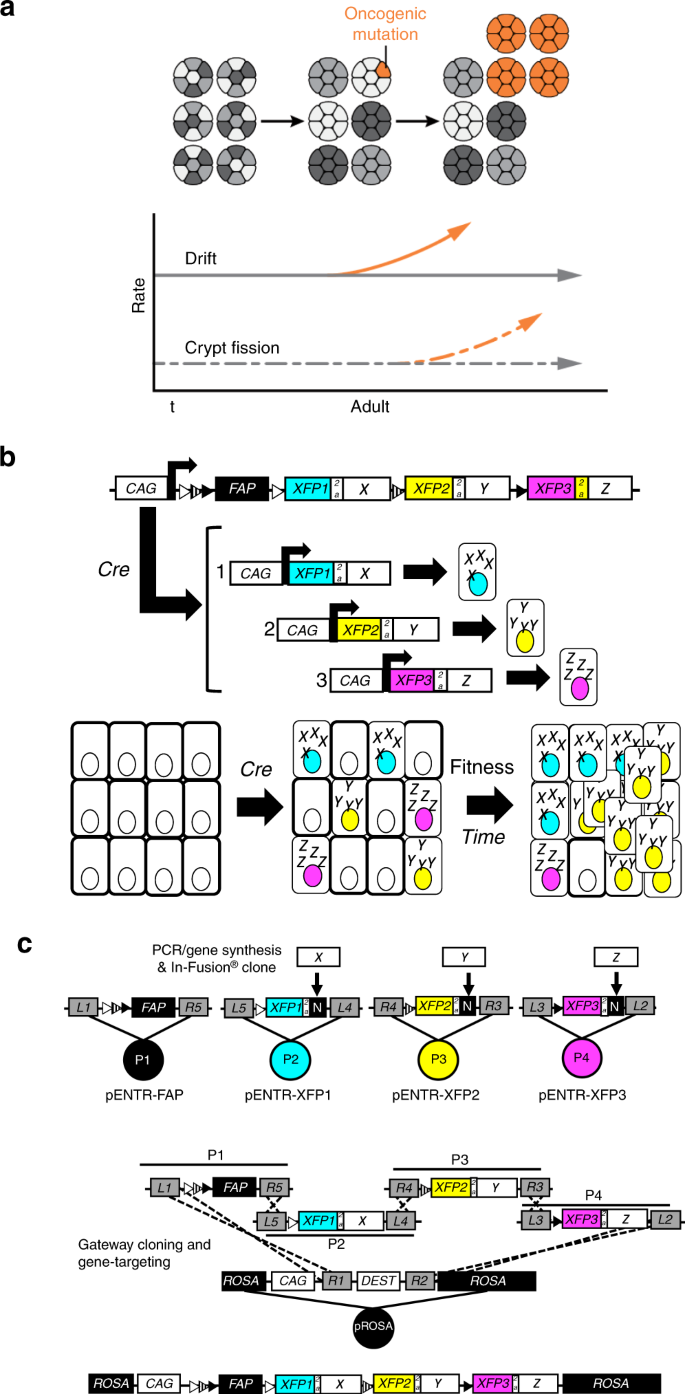


A Cancer Rainbow Mouse For Visualizing The Functional Genomics Of Oncogenic Clonal Expansion Nature Communications
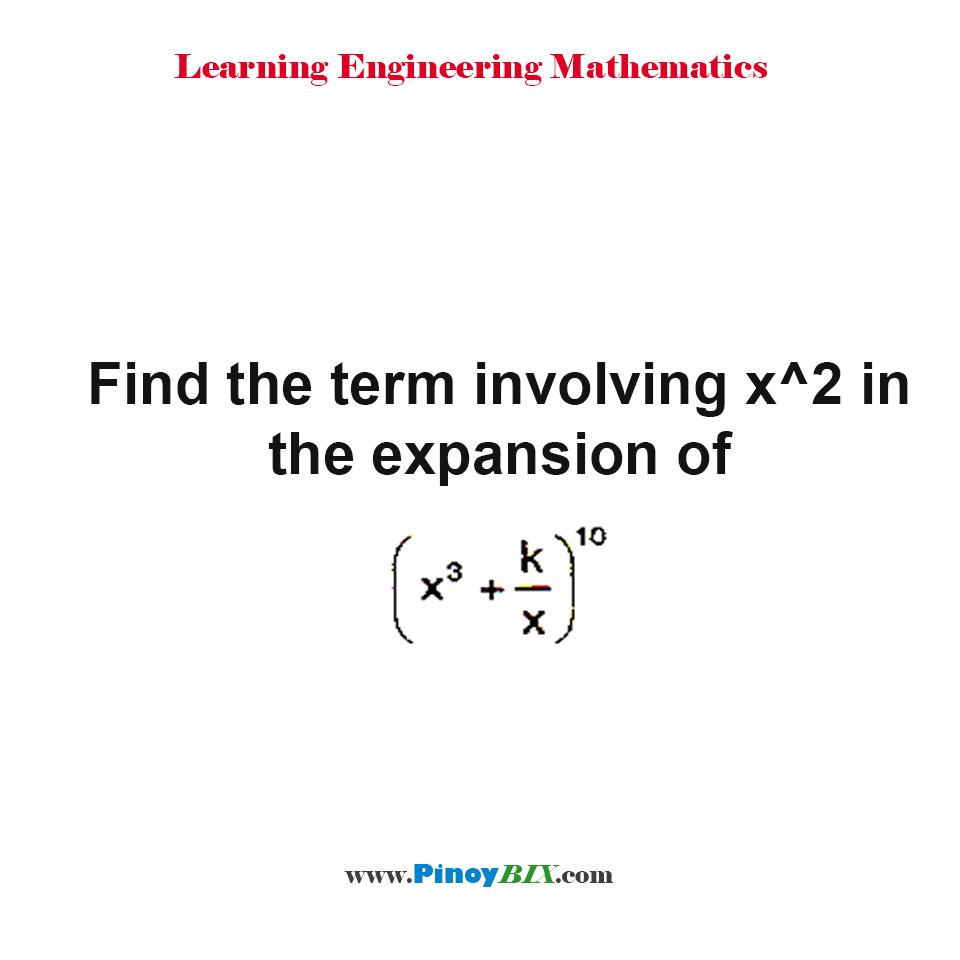


Solution Find The Term Involving X 2 In The Expansion Of X 3 K X 10
Polynomial Identities When we have a sum (difference) of two or three numbers to power of 2 or 3 and we need to remove the brackets we use polynomial identities (short multiplication formulas) (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Example 1 If x = 10, y = 5aStatistics Alternate variance formulas Sal explains a different variance formula and why it works!Expand each of the following using suitable identities X 2 Y 4 Z whole square Get the answers you need, now!


Least Common Multiple Of Polynomials Video Khan Academy



Mcq In Math
The intersection of the two spheres is a circle perpendicular to the x axis, at a position given by x above Substituting this into the equation of the first sphere gives y 2 z 2 = 4 d 2 r 12 (d 2 r 22 r 12) 2 / 4 d 2 You might recognise this is the equation of a circle with radius h whereView more examples »Exercise 3 Expand the following expression, writing your answer in its simplest form Be careful of notation and do not use spaces in your answer ( x ) 2 = x2 x



The Binomial Theorem Fractional Powers Expanding 1 2x 1 3 Youtube



Perfect Square Factorization Intro Video Khan Academy
= ( Σ (xμ)²= ( (Σ x²) / N ) μ²I√2/2, where the pluses and minuses can be taken in any order They are the four points at the intersections of the diagonal lines y = x and y = x with the unit circle We'll see them later as square roots of


Tools Vectornator Learn



Expand 2x 3y 2z 2 Brainly In
) / N Another equivalent formula is σ²It is 1/4*base2*(vertical height)2 in units of length to the fourth power If the lengths of the sides are X, Y and Z, then the area squared is (X Y Z)*( X Y Z)*(X Y Z)*(X Y Z)/16To simplify your expression using the Simplify Calculator, type in your expression like 2(5x4)3x The simplify calculator will then show you the steps to help you learn how to simplify your algebraic expression on your own Typing Exponents Type ^ for exponents like x^2 for x squared


Ambiguous Pemdas



Ex 2 5 4 Expand Each Of The Following Using Suitable
Isaac Newton wrote a generalized form of the Binomial Theorem However, for quite some time Pascal's Triangle had been well known as a way to expand binomials (Ironically enough, Pascal of the 17th century was not the first person to know aboutExpand and simplify an expression The calculator allows you to expand and collapse an expression online , to achieve this, the calculator combines the functions collapse and expand For example it is possible to expand and reduce the expression following ( 3 x 1) ( 2 x 4), The calculator will returns the expression in two forms expandedA 2 b 2 c 2 2 ×



Scalable And Isotropic Expansion Of Tissues With Simply Tunable Expansion Ratio Park 19 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library


Ambiguous Pemdas
Mar 16, 17Ex 25, 4 Expand each of the following, using suitable identities (x 2y 4z)2 (x 2y 4z)2 Using (a b c)2 = a2 b2 c2 2ab 2bc 2ac Where a = x , b = 2y, c = 4z = x2 (2y)2 (4z)2 2(x) (2y) 2(2y) (4z) 2 (4z) (x) = x2 4y2 16z2 4xy 16yz 8xz Ex 25, 4 Expand each of the following, using suitable identities (ii) (2x y z)2 (2x y z)2 = (2x ( y) z)2 Using (a b c)2 = a2 b2 c2 2ab 2bc 2ac Where a = 2x , b = y, c = z = (2x)2 (y)2 (z)2 2Students trying to do this expansion in their heads tend to mess up the powers But this isn't the time to worry about that square on the xI need to start my answer by plugging the terms and power into the TheoremThe first term in the binomial is x 2, the second term in 3, and the power n is 6, so, counting from 0 to 6, the Binomial Theorem gives meIntegrate x^2 sin y dx dy, x=0 to 1, y=0 to pi;
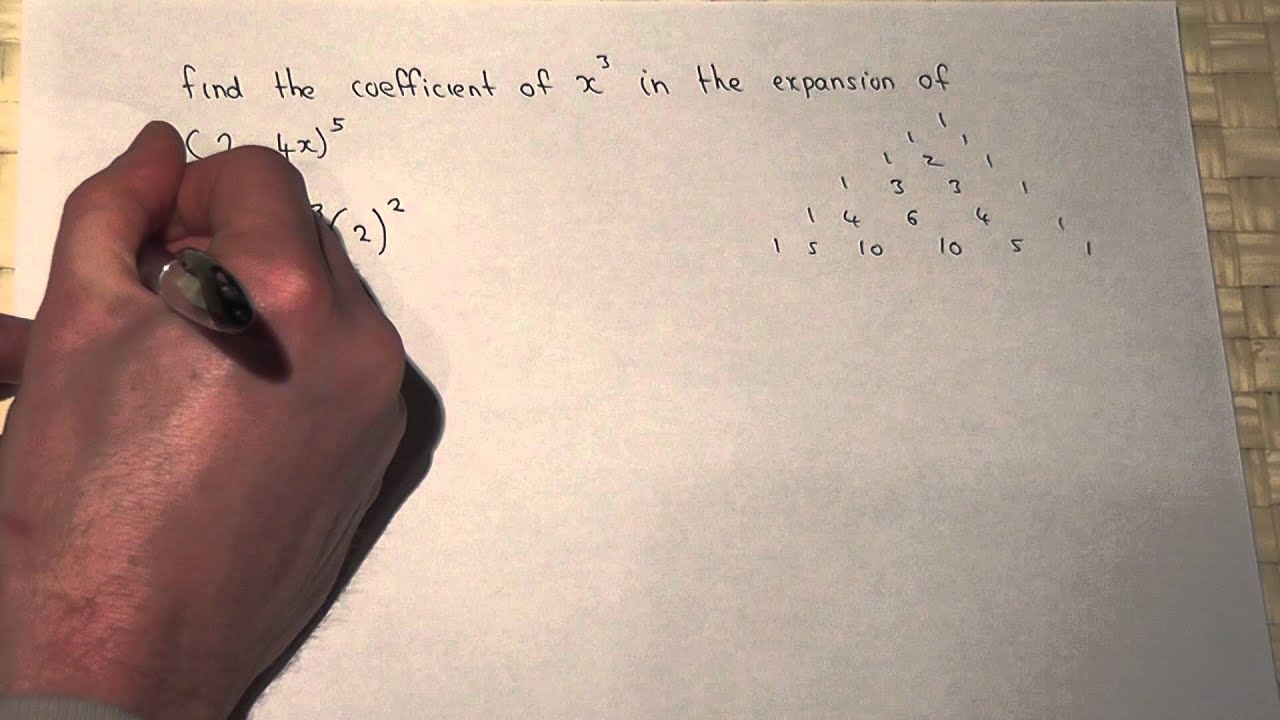


Binomial Theorem Finding The Coefficient Of X 3 In 2 4x 5 Youtube



Variance Wikipedia
Log b (x y) = y ∙ log b (x) For example log 10 (2 8) = 8∙ log 10 (2) Derivative of natural logarithm The derivative of the natural logarithm function is the reciprocal function When f (x) = ln(x) The derivative of f(x) is f ' (x) = 1 / x Integral of natural logarithm The integral of the natural logarithm function is given byPutting it all together, the steps are as follows ( x3 ) ( x4) = ( xxx ) ( xxxx) = xxxxxxx = x7 Then the simplified form of (x3) (x4) is x7 Note that x7 also equals x(34) This demonstrates the first basic exponent rule Whenever you multiply two terms with1 Identify the terms, their coefficients for each of the following expressions In the expression 5xyz 2 – 3zy, the terms are 5xyz 2 and –3zy coefficient of xyz 2 in the term 5xyz 2 is 5 coefficient of zy in the term –3zy is –3 In the expression 1 x x 2, the terms are 1, x and x 2



How To Expand Using The Identity A B C 2 B2 C2 2ab 2bc 2ca Youtube


If Z Is A Complex Number Then Is Z 2 Equal To Mod Z 2 Quora
For a population, the variance is calculated as σ²In algebra, a nested radical is a radical expression (one containing a square root sign, cube root sign, etc) that contains (nests) another radical expression Examples include 5 − 2 5 , {\displaystyle {\sqrt {52 {\sqrt {5}}\ }},} which arises in discussing theTo complete the square when a is greater than 1 or less than 1 but not equal to 0, factor out the value of a from all other terms For example, find the solution by completing the square for 2 x 2 − 12 x 7 = 0 a ≠ 1, a = 2 so divide through by 2 2 2 x 2 − 12 2 x 7 2 = 0 2 which gives us x 2 − 6 x 7 2



Find A If The Coefficients Of X 2and X 3in The Expansion Of


Rectangles Geom Raster Ggplot2
Two numbers r and s sum up to 4 exactly when the average of the two numbers is \frac{1}{2}*4 = 2 You can also see that the midpoint of r and s corresponds to the axis of symmetry of the parabola represented by the quadratic equation y=x^2BxCThe hyperbolic functions represent an expansion of trigonometry beyond the circular functionsBoth types depend on an argument, either circular angle or hyperbolic angle Since the area of a circular sector with radius r and angle u (in radians) is r 2 u/2, it will be equal to u when r = √ 2In the diagram, such a circle is tangent to the hyperbola xy = 1 at (1,1)Proving the Expansion of a plus b Whole Square Geometrically In this section, we are going to see, how to prove the expansion of (a b) 2 geometrically We can prove the the expansion of (a b) 2 using the area of a square as shown below Solved Problems Problem 1 Expand (x y) 2



Expand X By 2 Y 1 By 4 Whole Square Brainly In


Rectangles Geom Raster Ggplot2
Factorization goes the other way suppose we have an expression that is the difference of two squares, like x²25 or 49x²y², then we can factor is using the roots of those squares For example, x²25 can be factored as (x5)(x5) This is an extremely useful method that is used throughout mathThe Derivative Calculator will show you a graphical version of your input while you type Make sure that it shows exactly what you want Use parentheses, if necessary, e g a/ (bc)A complex number z = x yi will lie on the unit circle when x 2 y 2 = 1 Some examples, besides 1, –1, i, and –1 are ±√2/2 ±



The Term Independent Of X In Expansion Of X 1 X 2 3 X 1



X Y Whole Square X Y Whole Square Brainly In
Integrate x/(x1) integrate x sin(x^2) integrate x sqrt(1sqrt(x)) integrate x/(x1)^3 from 0 to infinity;X3=5 1/3 1/4 y=x^21 Disclaimer This calculator is not perfect Please use at your own risk, and please alert us if something isn't working Thank youEnter your queries using plain English To avoid ambiguous queries, make sure to use parentheses where necessary Here are some examples illustrating how to ask about factoring factor quadratic x^27x12 expand polynomial (x3) (x^35x2) GCD of x^42x^39x^246x16 with x^48x^325x^246x16 quotient of x^38x^217x6 with x3



Use Suitable Identities To Find The Following Products I X 4 X 10 Ii X 8 X 10 Ii Youtube



Expand Using The Identity A 2x 3y Z 2 Brainly In
Jan , 17Explanation Expansion of (a b)n gives us (n 1) terms which are given by binomial expansion xnCra(n−r)br, where r ranges from n to 0 Note that powers of a and b add up to n and in the given problem this n = 5 In (x − 3y)5, we need coefficient of x3y2, we have 3rd power of x and as such r = 5 −3 = 2 and as such the desiredFree Complete the Square calculator complete the square for quadratic functions stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this website, you agree to our Cookie PolicyClick here 👆 to get an answer to your question ️ Expand (x2y3z)²


Rectangles Geom Raster Ggplot2



Rd Sharma Solutions For Class 7 Maths Chapter 7 Algebraic Expressions Download Free Pdf
In algebra, a quadratic equation (from the Latin quadratus for square) is any equation that can be rearranged in standard form as = where x represents an unknown, and a, b, and c represent known numbers, where a ≠ 0If a = 0, then the equation is linear, not quadratic, as there is no term The numbers a, b, and c are the coefficients of the equation and may be distinguished by callingEnter the function you want to differentiate into the Derivative Calculator Skip the f (x) = part!Integrate 1/(cos(x)2) from 0 to 2pi;



2 X Square Y Square 8 Z Square 2 Root 2 X Y 4 Root 2 Y Z 8 X Z Brainly In



Factoring Using The Difference Of Squares Pattern Video Khan Academy
4 Binomial Expansions 41 Pascal's riTangle The expansion of (ax)2 is (ax)2 = a2 2axx2 Hence, (ax)3 = (ax)(ax)2 = (ax)(a2 2axx2) = a3 (12)a 2x(21)ax x 3= a3 3a2x3ax2 x urther,F (ax)4 = (ax)(ax)4 = (ax)(a3 3a2x3ax2 x3) = a4 (13)a3x(33)a2x2 (31)ax3 x4 = a4 4a3x6a2x2 4ax3 x4 In general we see that the coe cients of (a x)nThe calculator will find the binomial expansion of the given expression, with steps shown Show Instructions In general, you can skip the multiplication sign, so 5 x is equivalent to 5 ⋅ x In general, you can skip parentheses, but be very careful e^3x is e 3 x, and e^ (3x) is e 3 x Also, be careful when you write fractions 1/x^2 ln (xJan 24, 18You can't, really While it looks like you can just cancel out the squares with the square root, this only works if you have one square within the radical Since we're adding two together, it's slightly different There's no way to factor x^2y^2 to get a perfect square The only real way to simplify this expression is by using math that's at a higher than algebra level, so for all
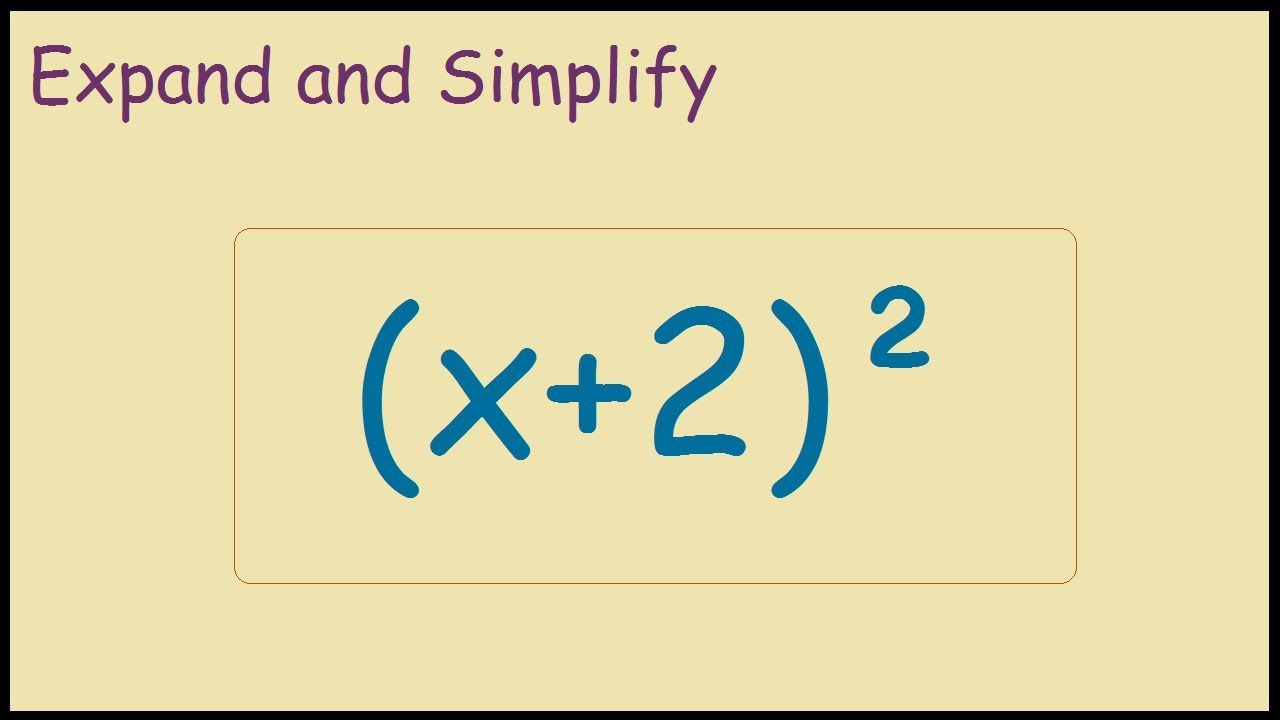


X 2 2 Expand And Simplify Using Foil Method Youtube



Multipole And Multimode Engineering In Mie Resonance Based Metastructures
Access instant learning tools Get immediate feedback and guidance with stepbystep solutions and Wolfram Problem Generator LearnExpand Using the Binomial Theorem (XY)^4 Use the binomial expansion theorem to find each term The binomial theorem states Expand the summation Simplify the exponents for each term of the expansion Simplify each term Tap for more steps Multiply by Anything raised to isSimplify calculator Expand and simplify equations stepbystep This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience By using this



Scalable And Isotropic Expansion Of Tissues With Simply Tunable Expansion Ratio Park 19 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library


Covid Economics Centre For Economic Policy Research
Expand (x 2 3) 6;Algebra Calculator is a calculator that gives stepbystep help on algebra problems See More Examples »Mathematics Menu The following are algebraix expansion formulae of selected polynomials Square of summation (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Square of difference (x y) 2 = x 2 2xy y 2 Difference of squares



X Y Z Whole Square Formula A Pictures Of Hole 18
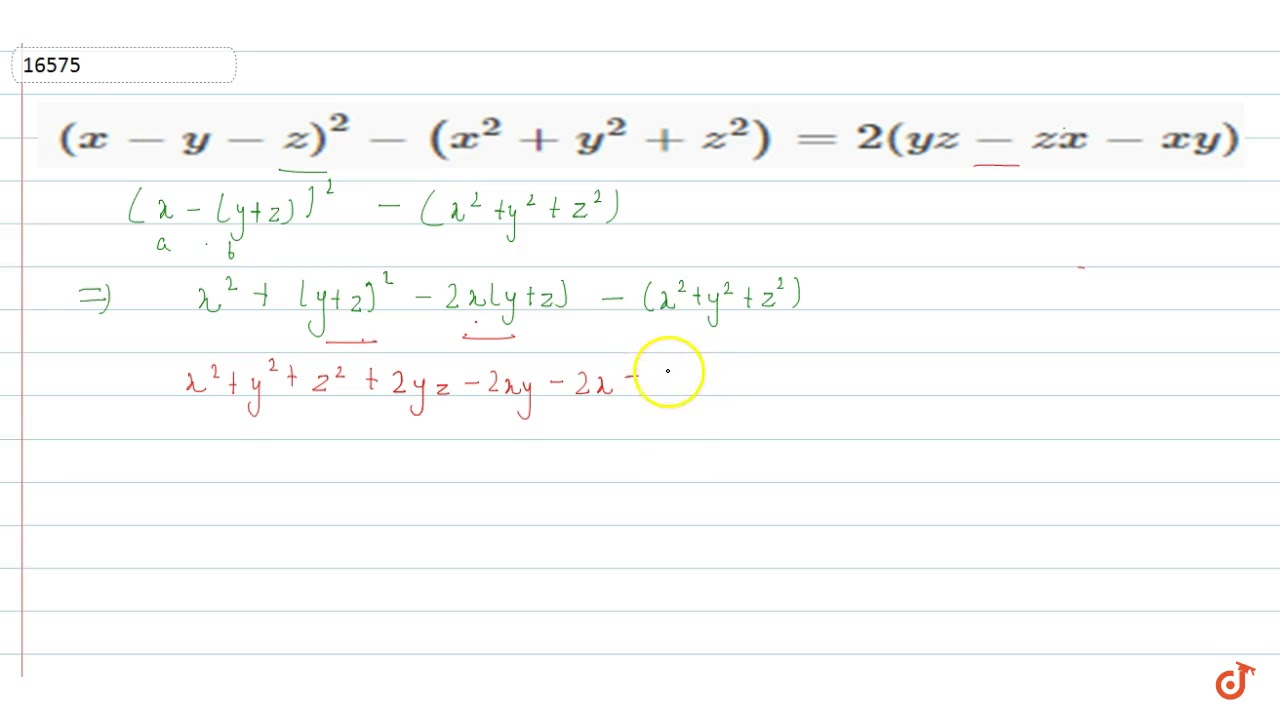


X Y Z 2 X 2 Y 2 Z 2 2 Yz Zx Xy Youtube



A Guide To Elegant Tiled Heatmaps In R 19 Rmf



Using Binomial Theorem Write Down The Expansion Of 2x 3y 5
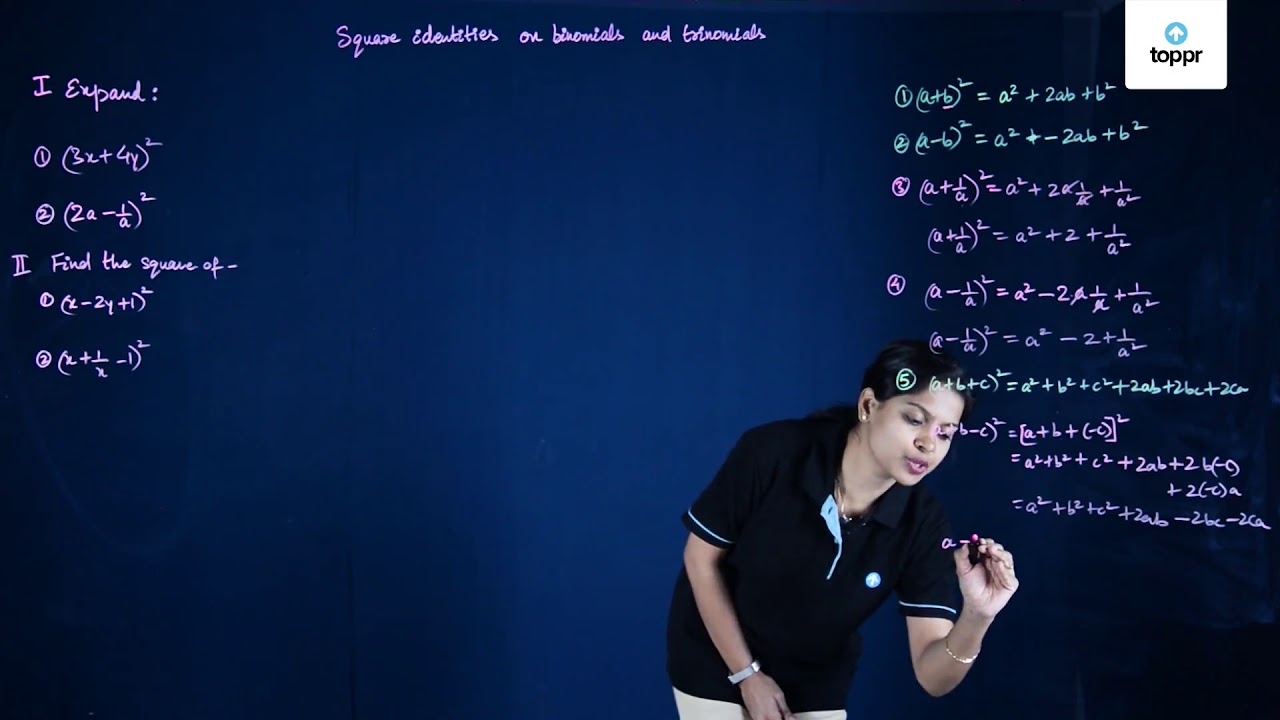


Standard Identities Of Binomials And Trinomials Equations Examples
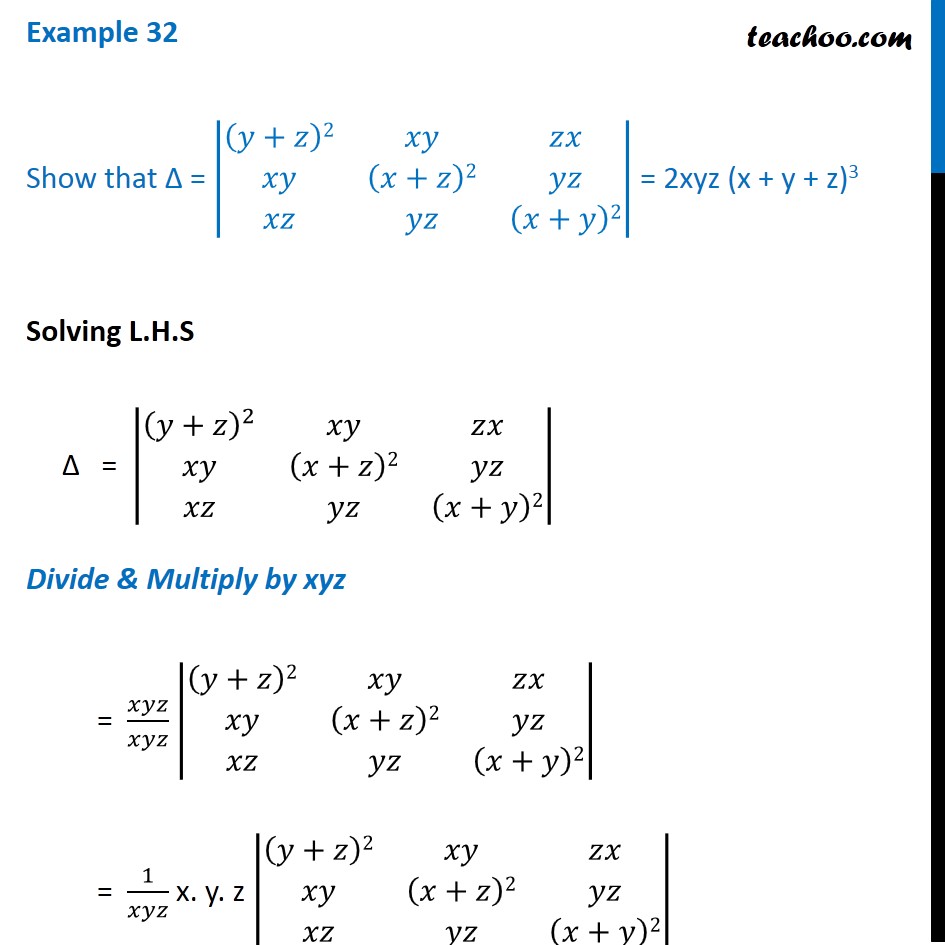


Example 32 Show That Determinant 2xyz X Y Z 3 Class 12



Numbers In Python Real Python
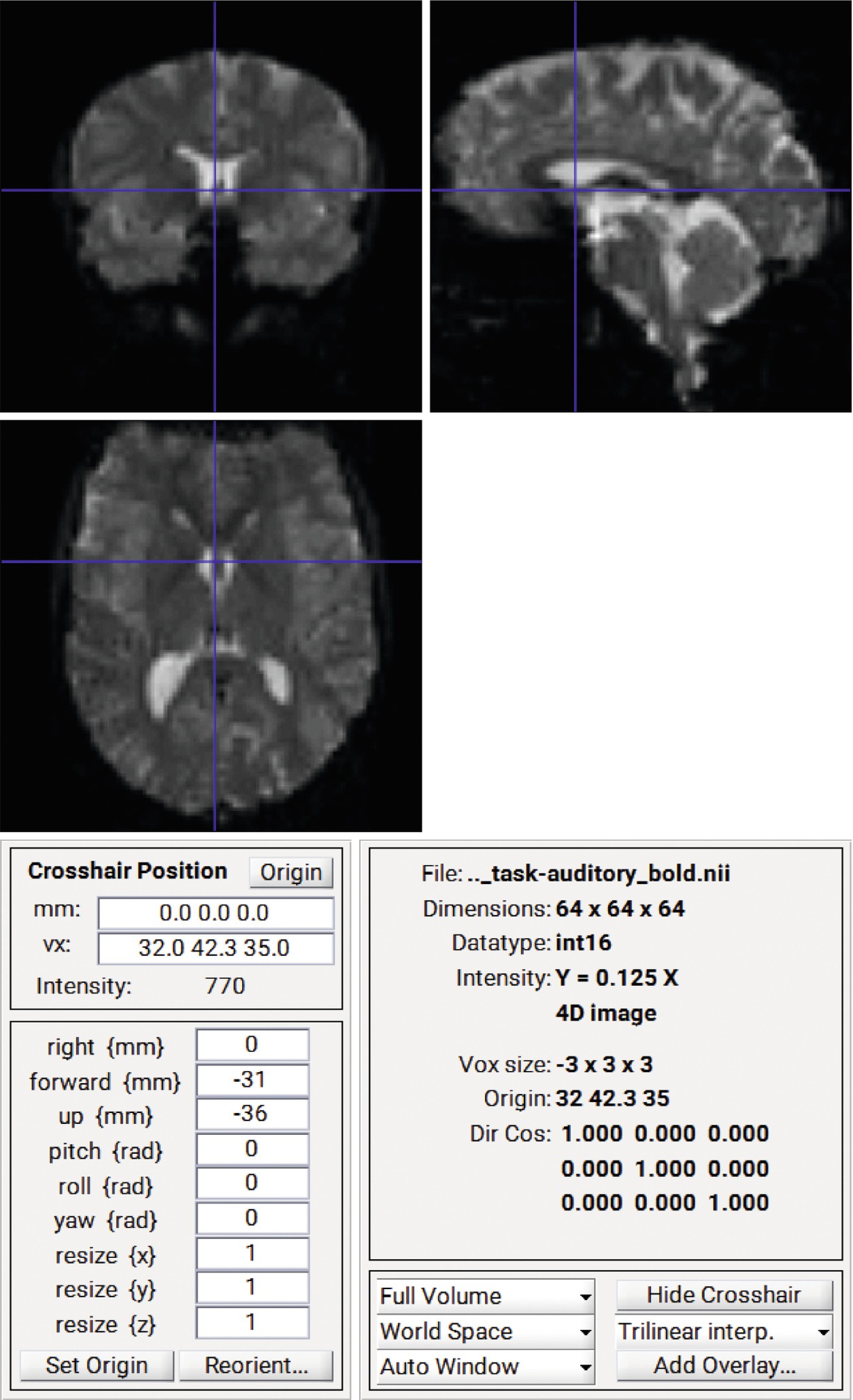


Fmri Data Analysis Using Spm Springerlink



Ex 2 5 4 Expand Each Of The Following Using Suitable



Expand Form Of X Y Z Whole Square Brainly In
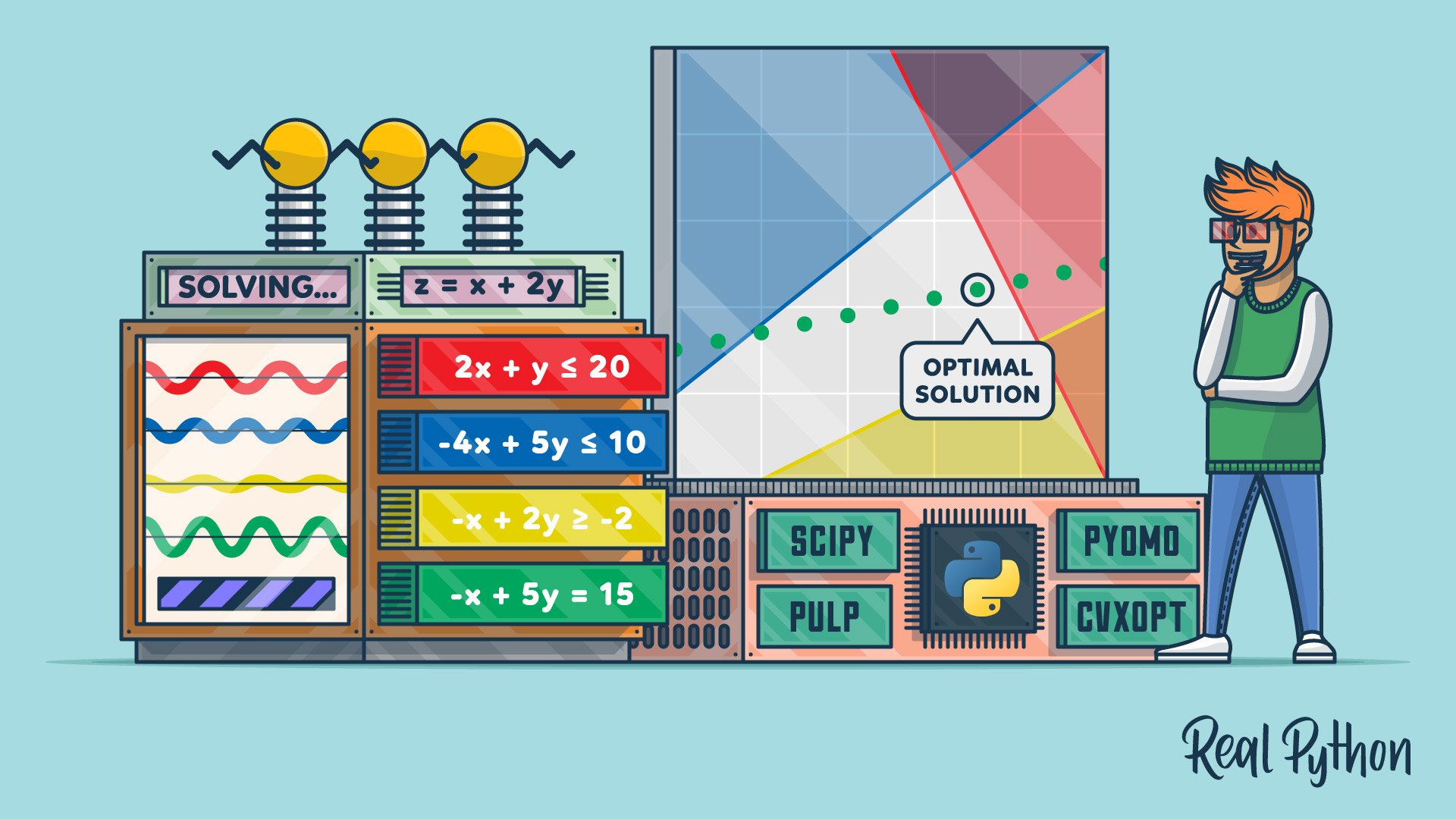


Hands On Linear Programming Optimization With Python Real Python
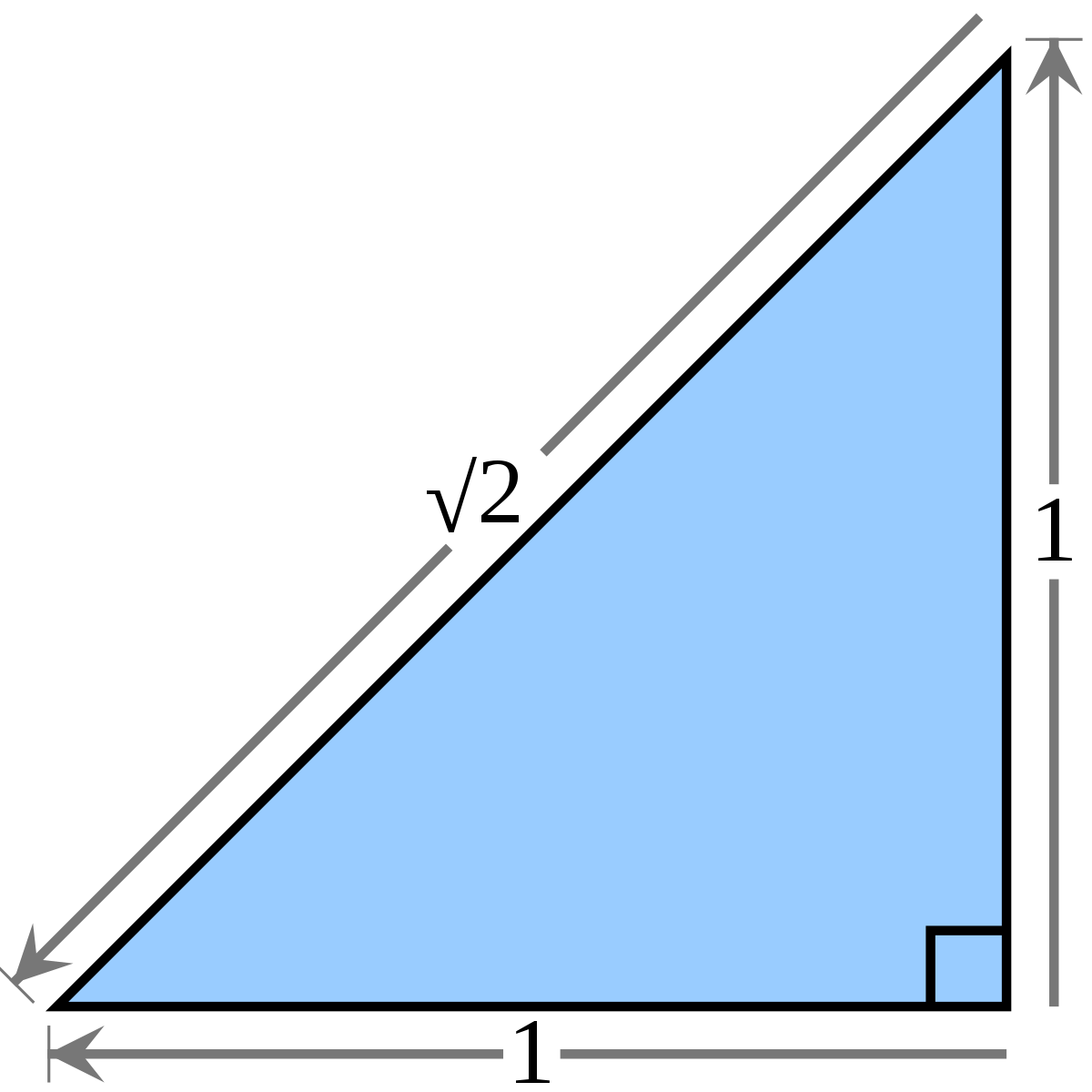


Square Root Of 2 Wikipedia
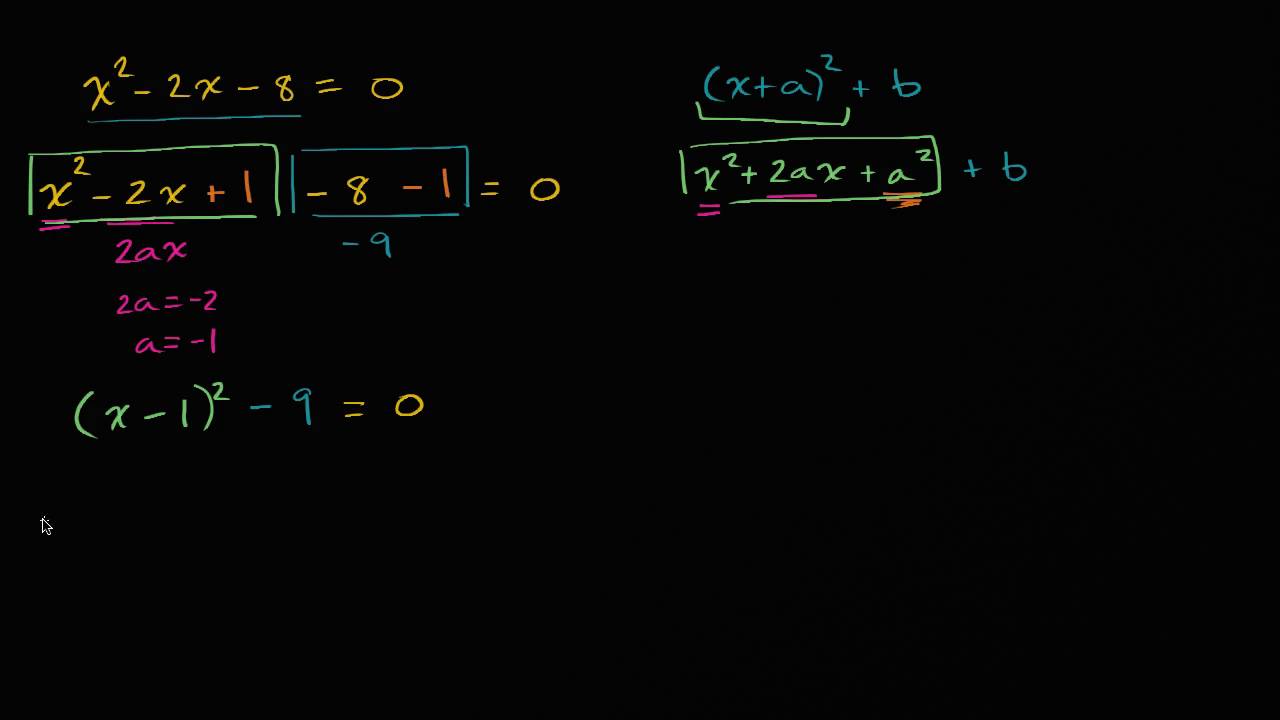


Worked Example Rewriting Solving Equations By Completing The Square Video Khan Academy


Rectangles Geom Raster Ggplot2



The Sum Of The Co Efficients Of All The Even Powers Of X In The Expansion Of 2x 2 3x 1 11 Is



Expand X 2 Y 1 4 2 Brainly In



Simplifying Square Root Expressions Video Khan Academy



Ex 2 5 4 Expand Each Of The Following Using Suitable



X Square Minus Y Square Whole Cube Y Square Minus Z Square Whole Cube Z Square Minus Y Square Brainly In


Riemann Zeta Function Wikipedia


Space And Meaning Tobias Bernard S Gnome Blog



Example 7 Find Coefficient Of X6y3 In Expansion X 2y 9



Ex 2 5 4 Expand Each Of The Following Using Suitable



Write The Coefficient Of Y In The Expansion Of 5 Y 2 Brainly In



The Binomial Theorem Explained With A Special Splash Of Pascal S By Brett Berry Math Hacks Medium



The Factors Of X 2 4y 2 4y 4x Y 2x 8 Are A X 2y 4 X 2y 2 B X Y 2 X 4y 4 C Youtube



Square Algebra Wikipedia



Find The Coefficient Of X 6y 3in The Expansion Of X 2y



Expand 1 X X 2 3



If Number Of Terms In The Expansion Of X 2y 3z N Are 45 Th



Find The Value Of X Cube Y Cube Z Cube Minus 3 X Y Z If X Square Y Square Z Square Is Equal To Brainly In


Ambiguous Pemdas



Example 19 Write 3a 4b 5c 2 In Expanded Form Examples



Ex 8 2 3 Write General Term In X2 Y 6 Chapter 8 Ex 8 2


Taylor Series Wikipedia



Factorise X Square 2xy Y Square Z Square Brainly In
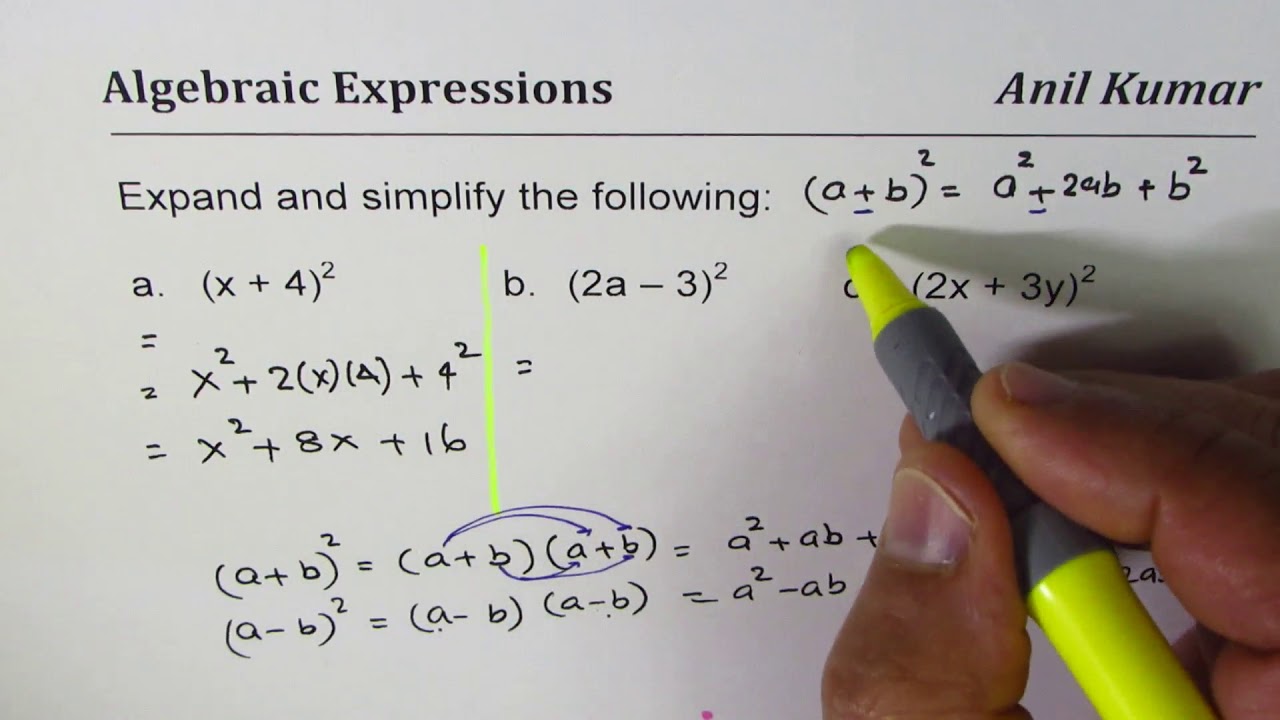


Expand And Simplify Binomial Squares 2x 3y 2 Youtube
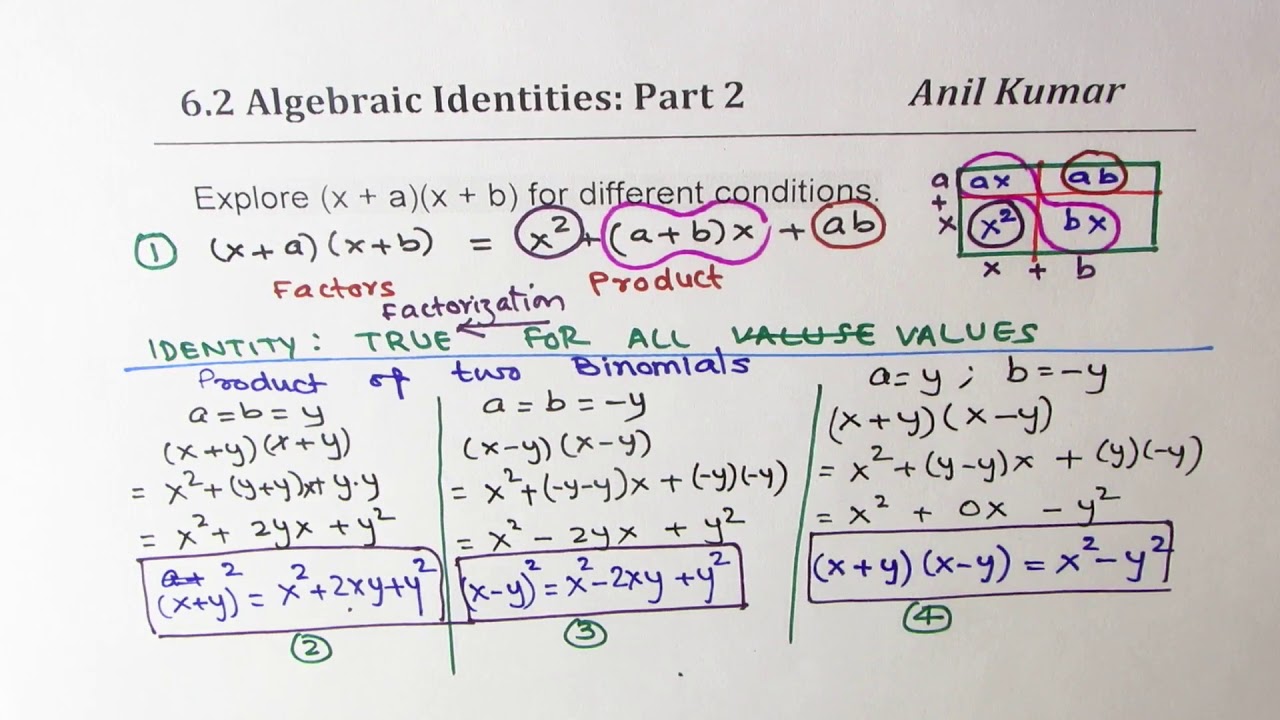


Expand And Simplify Binomial Squares 2x 3y 2 Youtube


Taylor Series Wikipedia


Sketch The Interface



Product X 2 2y X 2 4 Xy 4y 2 Brainly In


How Did Urban Land Expand In China Between 1992 And 15 A Multi Scale Landscape Analysis



Ex 8 1 1 Expand 1 2x 5 Chapter 8 Class 11 Binomial



Algebra Formulas For Class 10 Download Algebraic Identities For Class 10 Pdf
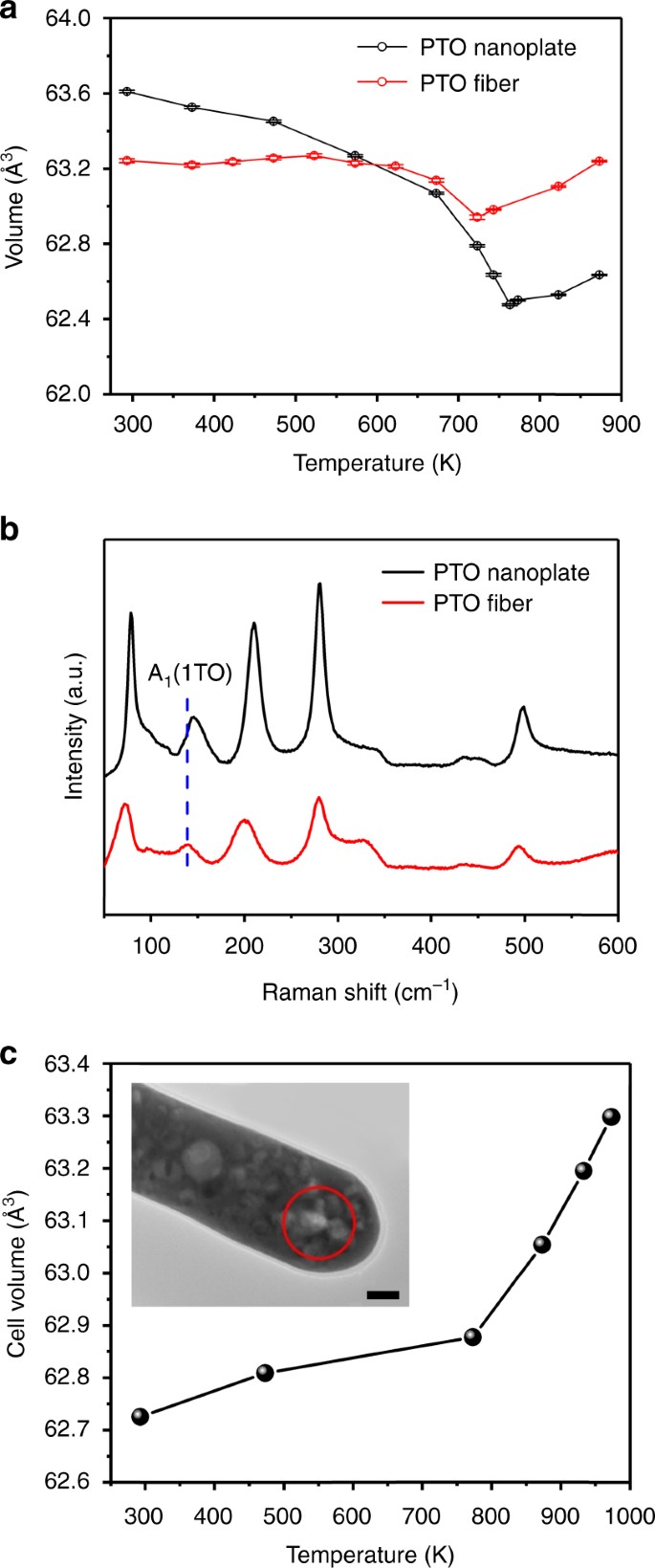


Mesopores Induced Zero Thermal Expansion In Single Crystal Ferroelectrics Nature Communications



Active Noise Attenuation In Ventilation Windows The Journal Of The Acoustical Society Of America Vol 130 No 1



Example 7 Find Coefficient Of X6y3 In Expansion X 2y 9



Expand Using Identities 3x 5y 2
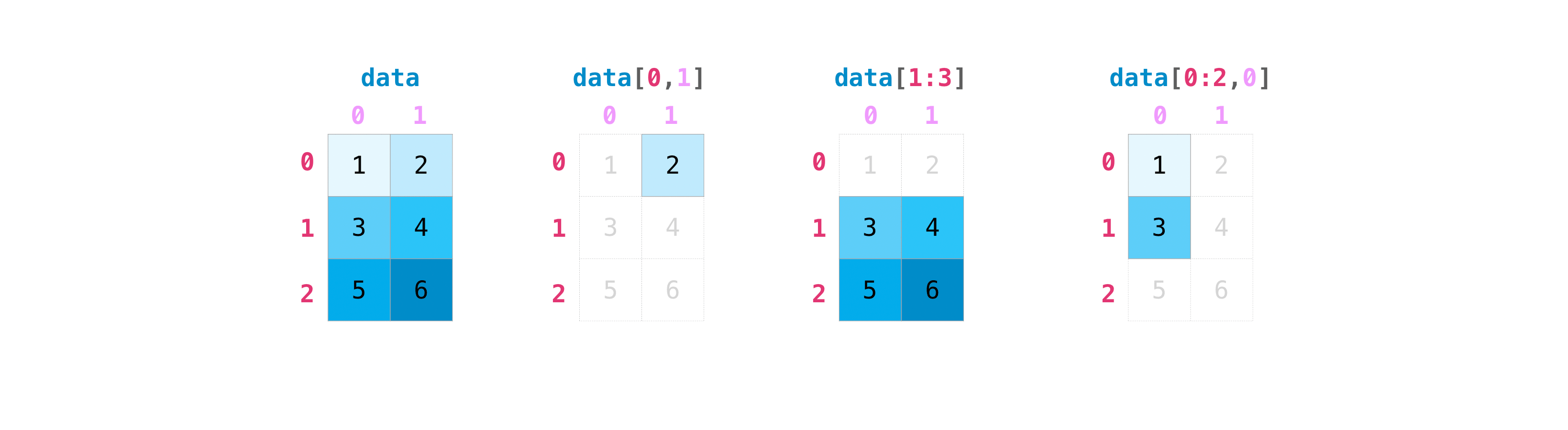


Numpy The Absolute Basics For Beginners Numpy V1 21 Dev0 Manual



Partial Fraction Expansion Repeated Factors Video Khan Academy



Example 21 Factorize 4x2 Y2 Z2 4xy 2yz 4xz Examples
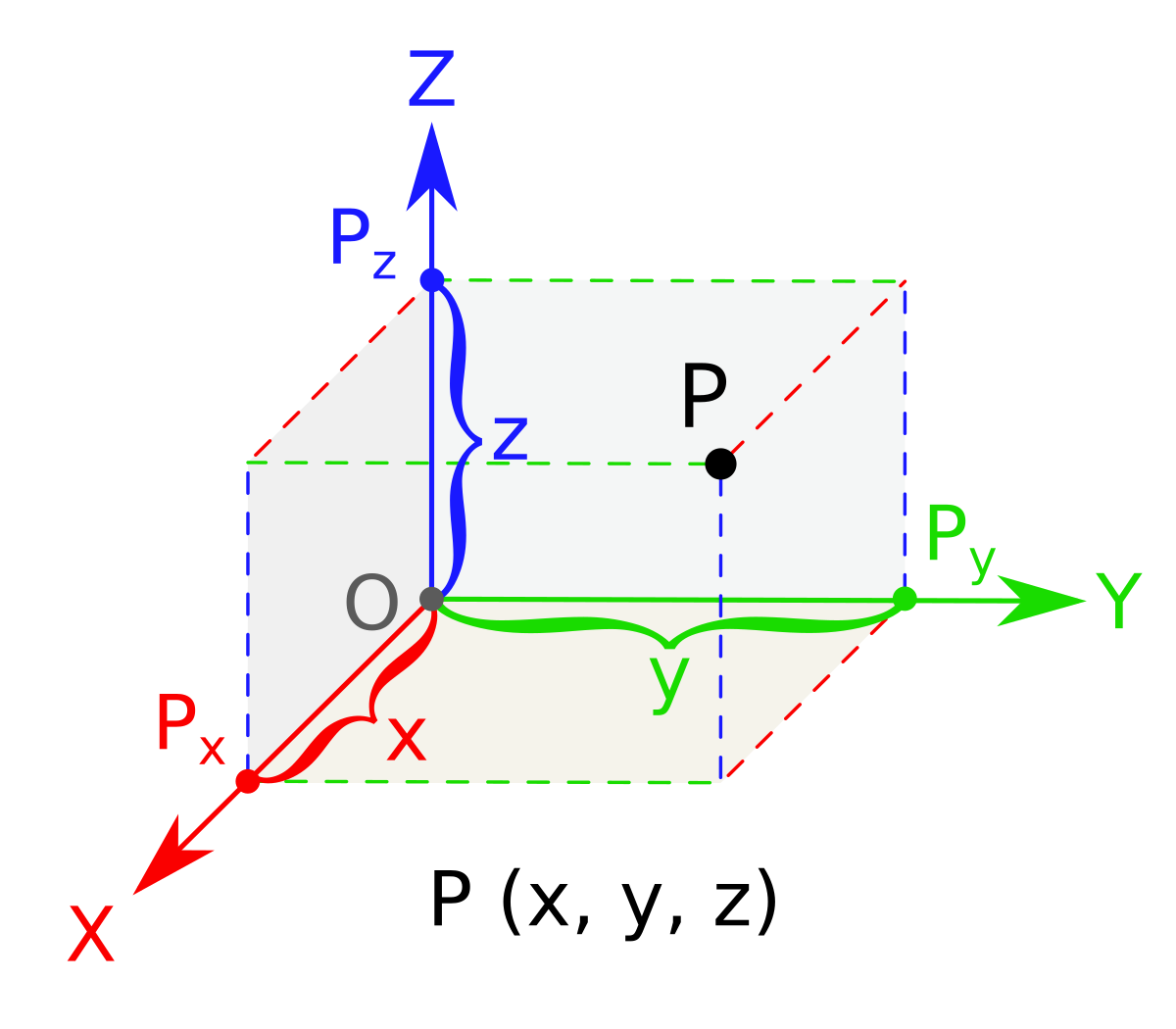


Three Dimensional Space Wikipedia
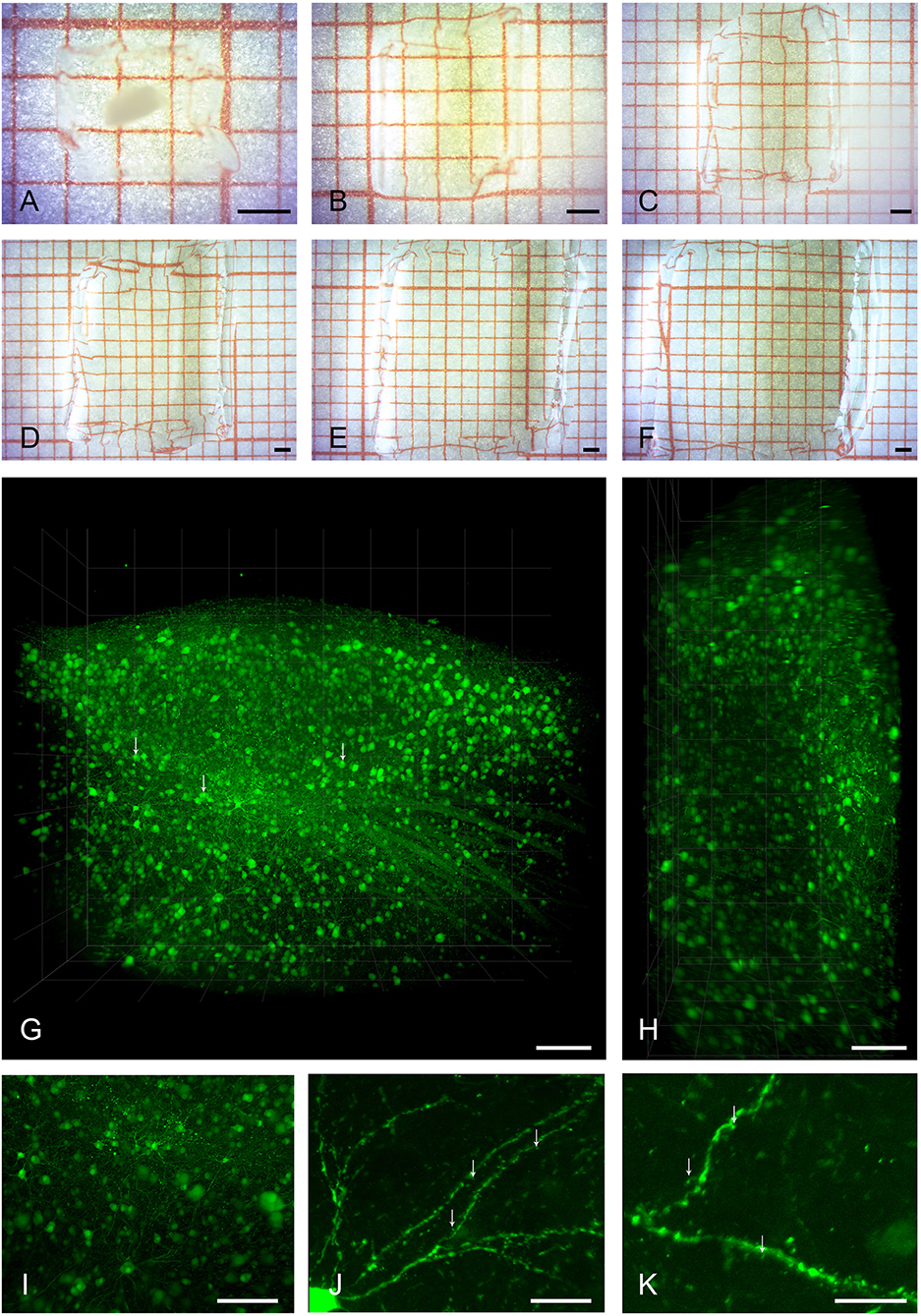


Frontiers Expansion Light Sheet Microscopy Resolves Subcellular Structures In Large Portions Of The Songbird Brain Frontiers In Neuroanatomy



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿